Getting lost in cloud service models IaaS PaaS SaaS? You’re not alone.
Each model affects your costs, control, and flexibility. Choose wrong, and you could be wasting time, money, and momentum.
Did you know the global cloud market is set to hit $679B in 2024 (Statista)? Businesses everywhere are embracing the cloud shift. The real question is: Which model is right for you?
By the end of this guide, you’ll understand what each model offers and know exactly which aligns with your business goals, your team, and your future.
Let’s get started.
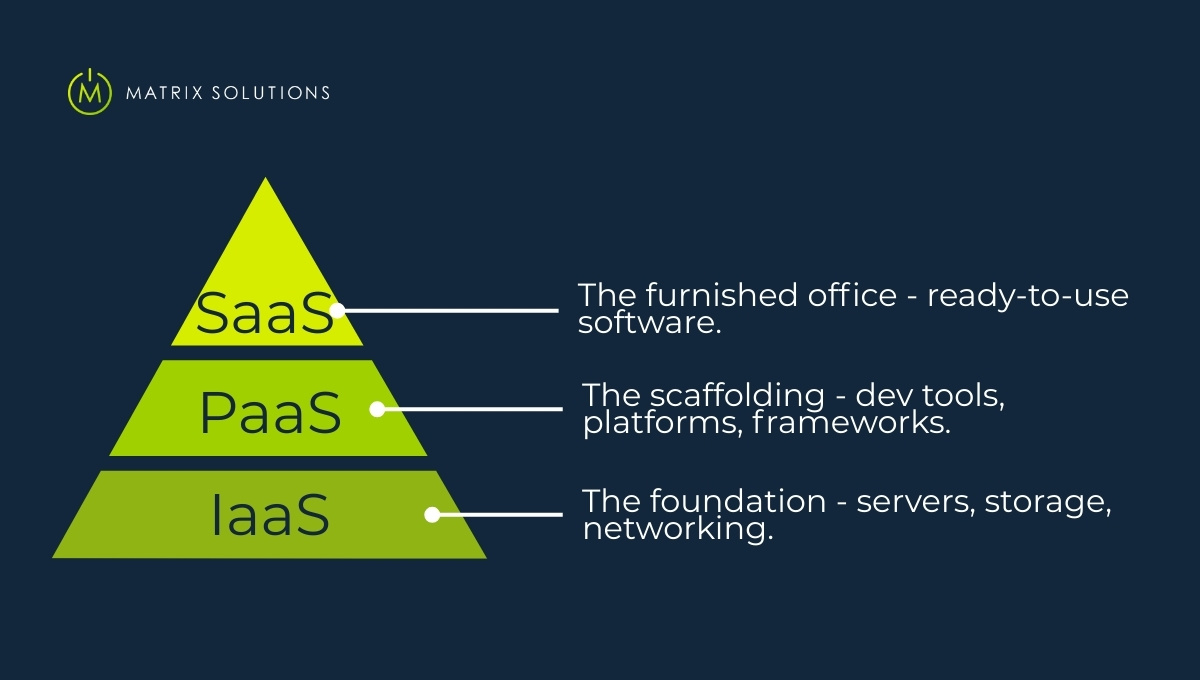
What is PaaS, IaaS and SaaS?
Cloud computing, often delivered through managed IT solution, has transformed the whole range of business operations. But not every cloud solution fits every need, and knowing the basic service models is crucial for navigating the landscape:
- PaaS: PaaS stands for Platform as a Service
- IaaS: IaaS means Infrastructure as a Service
- SaaS: SaaS stands for Software as a Service
Each of these models has its own functions, with different levels of control, flexibility, and management accountability. Together, IaaS PaaS SaaS cover the full range of cloud services, from raw infrastructure to ready-to-use software.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
Platform as a Service (PaaS) provides a cloud environment that allows businesses to develop, run, and manage applications efficiently without managing the underlying infrastructure. It is designed for your developers to concentrate on what they do best: coding and innovating. PaaS eases application development by providing tools, frameworks, and services to build and deploy applications effectively.
PaaS Characteristics:
These core features make PaaS ideal for agile development teams and innovation-focused businesses:
- Cloud-based development platform
- Application development, deployment, and maintenance support
- Scalability and flexibility
- Pre-configured software tools and frameworks
PaaS Delivery: As the name suggests, it is delivered entirely through the cloud. This includes an optional subscription-based service with various features and tools for software development.
PaaS Benefits and Disadvantages
Like any tech solution, PaaS brings both advantages and trade-offs.
Pros | Cons |
Easy app deployment | Limited control over infrastructure |
Reduced infrastructure costs | Risk of vendor lock-in |
Scalable, flexible solutions | Not ideal for highly customised apps |
When to Use PaaS?
PaaS is the go-to solution when you want to build and deploy apps quickly without spending time or resources on configuring and maintaining infrastructure. It’s particularly beneficial for:
- Developers needing a flexible coding environment
- Businesses that need to scale applications on demand
- Teams focused on rapid product iteration or MVP delivery
Best Use Cases for PaaS
|
Best For |
Examples |
|
Software developers |
Google App Engine, Heroku |
|
Startups and SMEs |
Microsoft Azure, IBM Cloud Foundry |
|
Businesses with fast deployment needs |
Red Hat OpenShift, Oracle Cloud Platform |
|
Scalable business applications |
AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Cloud Foundry |
SaaS (Software as a Service)
Software as a Service (SaaS) application packages are delivered to the user over the web media. It removes the need for installing, operating, and maintaining software commonly on user devices. The entire application stack is managed, hosted, secured, updated, and even supported by the SaaS provider.
Individuals and businesses can access software on demand with just an internet connection. This makes SaaS an ideal choice for today’s fast-paced, remote-ready work environments where agility, flexibility, and accessibility are essential.
SaaS Characteristics
The features that make SaaS the simplest and most accessible cloud model for end users include:
- Hosted and managed by a third-party provider
- Accessed via web browser or API
- Subscription or pay-as-you-go pricing
- No installation or maintenance required
SaaS Delivery:
SaaS application delivery is one hundred percent through internet access, performed via a browser or via a client interface. The vendor handles everything related to this application server infrastructure, maintenance, data security, and updates.
SaaS Benefits and Disadvantages
Let’s look at some of the benefits and drawbacks of the SaaS model:
|
Pros |
Cons |
|
No installation or maintenance required |
Limited customisation |
|
Accessible from anywhere |
Data security depends on provider |
|
Cost-effective and scalable |
Internet dependency |
When to Use SaaS?
Choose SaaS when you need fast and reliable access to common business applications without the hassle of infrastructure, development, or maintenance. This is a good fit for:
- Companies looking for plug-and-play solutions
- Businesses with limited IT staff
- Teams that need collaboration and productivity tools wherever they are.
Best Use Cases for SaaS
SaaS is best for organisations that want quick access to standardised, business-critical software without technical overhead.
Best For | Examples |
Remote teams and digital workplaces | Microsoft 365, Google Workspace |
Customer relationship management (CRM) | Salesforce, Zoho CRM |
Small businesses and startups | Xero, Canva, Dropbox |
Enterprise communication and productivity | Slack, Zoom, Notion |
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides on-demand access to essential IT resources such as virtual servers, storage, and networking over the internet. This empowers enterprises to scale their infrastructure quickly, without investing in physical hardware, offering flexibility, cost-efficiency, and greater control over computing environments.
IaaS provides the highest level of flexibility and scalability among all other cloud services. It befits IT admins, DevOps teams, and enterprises that have extensive infrastructure requirements.
IaaS Characteristics
Some core features of IaaS are:
- Virtualised hardware: servers, storage, and networks
- On-demand resource provisioning
- Highly scalable and elastic
- User manages OS, applications, and runtime
IaaS Delivery:
IaaS is offered through the cloud in a self-service, pay-as-you-go model. Users can provision and manage virtual machines and resources through a web portal or API while the provider handles the physical infrastructure.
IaaS Benefits and Disadvantages
IaaS offers maximum control, but with great power comes greater responsibility. Here are its pros and cons:
|
Pros |
Cons |
|
Full control over infrastructure |
Requires technical expertise |
|
Scalable to match business growth |
Higher management overhead |
|
Cost-efficient for dynamic workloads |
Potential for over-provisioning |
When to Use IaaS?
Opt for IaaS when your business demands total control over its computing environment, with the flexibility to build, scale, and manage your own systems. It’s perfect for:
- Companies with internal IT teams
- Projects that need personalised configurations
- Workloads that fluctuate and demand scalability
Best Use Cases for IaaS
IaaS is ideal for businesses that need tailored environments, complete control, or large-scale infrastructure.
Best For | Examples |
IT departments and system admins | Amazon EC2, Microsoft Azure VMs |
High-traffic websites or apps | Google Compute Engine, IBM Cloud Infrastructure |
Disaster recovery and backups | Rackspace, Oracle IaaS |
Enterprises with complex IT environments | Alibaba Cloud, DigitalOcean |
Key Differences Between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
Here are some key differences between cloud service models: IaaS PaaS Saas.
Aspect | IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) | PaaS (Platform as a Service) | SaaS (Software as a Service) |
Primary Offering | Basic building blocks like virtual machines, storage, and networks. | A ready-to-use platform to build, test, and launch apps. | Complete software tools like email, CRM, or file sharing. |
Control Level | Full control over systems, software, and the setup. | Some control – you manage your app but not the platform itself. | Little to no control – everything is managed for you. |
Target Audience | IT teams and tech-savvy users who want total flexibility. | Developers who want to code without worrying about infrastructure. | Everyday users or businesses that just want ready-made tools. |
Management | You handle everything – the operating system, apps, and security. | You manage your app; the provider takes care of the backend. | The provider manages everything from top to bottom. |
Customisation Options | Highly flexible – tailor every piece to fit your needs. | Some flexibility within the tools and services offered. | Limited – what you see is what you get. |
Cost Structure | Pay only for the resources you use, like power and storage. | Usually, it’s a subscription, sometimes with extra charges based on usage. | Subscription-based with different plans or user tiers. |
Scalability | Very scalable – add or remove resources as you need. | Scalable but within the limits of the platform. | Scales easily with more users or features added. |
Best Use Cases | Running websites, setting up virtual servers, data backups. | Building and deploying custom apps quickly and easily. | Managing emails, sharing files, or using business tools. |
Real-Life Examples | AWS EC2, Google Compute Engine | Google App Engine, Azure App Service | Google Workspace, Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365 |
SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS: Which Cloud Model Is Right for Your Business?
Choosing between SaaS, PaaS, or IaaS isn’t about picking the “best” one – it’s about finding the right fit for your business goals, technical resources, and compliance needs. Here’s how to make that choice with confidence:
Business Size and IT Capability
- Small Businesses & Startups – SaaS
Perfect for teams with limited technical resources. SaaS solutions are easy to deploy, require no infrastructure management, and let you hit the ground running. - Growing Businesses with Developers – PaaS
Ideal for companies with in-house dev teams. PaaS offers a ready-to-use platform to build and deploy apps without the headache of managing servers or infrastructure. - Large Enterprises with Complex Needs – IaaS
Best suited for organisations that need full control over their IT environment. IaaS supports custom applications, legacy systems, and strict security or compliance requirements.
Compliance and Data Control
Compliance needs vary widely across industries, and choosing between IaaS PaaS SaaS often comes down to how much control your organization needs over data, infrastructure, and security.
- IaaS – Maximum Control for Regulated Industries
For sectors like legal, finance, or healthcare, where strict data governance is non-negotiable, IaaS offers complete control over data storage, security protocols, and compliance requirements. - SaaS – Convenient Compliance, If Certified
SaaS platforms can also meet industry standards, provided the provider holds key certifications such as ISO 27001, SOC 2, or HIPAA. Always verify their compliance credentials before committing. - Hybrid Approach – The Best of Both Worlds
Many organisations strike a balance by using SaaS for day-to-day operations (like email or CRM) and IaaS for sensitive data handling, ensuring both productivity and regulatory peace of mind.
Budget and Long-Term Plans
- SaaS: Low upfront cost – great for startups and quick deployment.
- PaaS: Saves time and money for teams building apps in-house.
- IaaS: Higher setup cost, but ideal for scalable, long-term growth.
Still Not Sure? Here's the Shortcut:
- Need full customisation? Go with IaaS.
- Want to develop custom apps quickly without infrastructure headaches? That’s PaaS.
- Prefer plug-and-play tools with no maintenance? SaaS is your answer.
Need guidance on choosing the right cloud model for your firm? Speak with a local expert – no pressure, just answers.
Matrix Solutions for Your Cloud Services
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and legal firms in Australia require more than just generic IT support; they need secure, scalable, and compliant cloud solutions tailored to their industry.
At Matrix Solutions, we specialise in delivering cloud infrastructure that aligns with business objectives, local compliance standards, and operational needs. Whether you need Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) for greater control, Platform as a Service (PaaS) to streamline development, or Software as a Service (SaaS) for easy collaboration, our solutions are designed for long-term impact. We help businesses navigate the full IaaS PaaS SaaS landscape with expert guidance and practical implementation.
We provide:
- End-to-end cloud solutions customised for legal and professional service industries
- Legal-grade data security and privacy controls that meet Australian compliance requirements
- Ongoing IT support from a local team that understands your business environment
Our clients choose Matrix Solutions because we go beyond technology. We offer trusted partnerships. With a strong local presence and proven track record in supporting Australian firms, we empower your business to operate confidently in the cloud.
Conclusion
Choosing the right iaas paas saas model is essential for aligning technology with your business goals. Each offers a unique balance of control, scalability, and convenience, depending on your needs and resources.
For smaller teams, SaaS delivers simplicity and speed. For more complex operations, Iaas and Paas provide flexibility and customisation. The right choice fuels innovation, resilience, and growth, so evaluate your priorities and let the cloud work for you.
People Also Ask these Questions
Which model is best for law firms in Australia?
A mix works best for law firms. Law firms often use SaaS for email and documents and IaaS for secure file storage and compliance.
What’s the main difference between these IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS cloud models?
The distinct difference between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS cloud models is about control. IaaS gives you full control. PaaS gives you control over apps. SaaS gives you the app, fully managed.
Can I use more than one model together?
Yes. You can use all three iaas paas saas models too! Many businesses combine models like using SaaS for email, PaaS for app development, and IaaS for storage.
Is SaaS secure enough for sensitive client data?
Yes, if the provider uses strong encryption and holds certifications like ISO 27001 or SOC 2.
Is Netflix a SaaS or PaaS?
Netflix is a SaaS. It provides video content as a service over the internet.
What are the four main types of cloud services?
IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, and XaaS (Everything-as-a-Service) are the main types of service models of cloud computing.
What’s an example of a real-world PaaS solution?
Google App Engine is a real-world PaaS that helps developers build and deploy apps without managing servers.




