ISO/IEC 27001 is a globally recognised standard for establishing an Information Security Management System (ISMS). It focuses on safeguarding information through strong security and privacy measures built around three core principles: confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA). In addition, data protection and cyber resilience are covered by more than a dozen standards in the ISO/IEC 27000 family.
Organisations from every sector and of all sizes use these standards to protect assets such as financial information, intellectual property, employee data, and confidential third-party information.
Lawyers, legal advocates, and law firms can benefit from implementing an Information Security Management System (ISMS) based on ISO/IEC 27001. It helps reduce the risk of data breaches and keeps client information safe. Following this standard also shows that the firm takes privacy and security seriously. It builds trust by proving that sensitive data is handled responsibly and in line with laws like the Privacy Act and GDPR.
In this blog post, we will discuss what ISO 27001 is, its importance, principles, domains, and how law firms can benefit from the certification under ISO 27001, and some common requirements of an ISMS based on ISO 27001.
The Evolution of ISO/IEC 27001
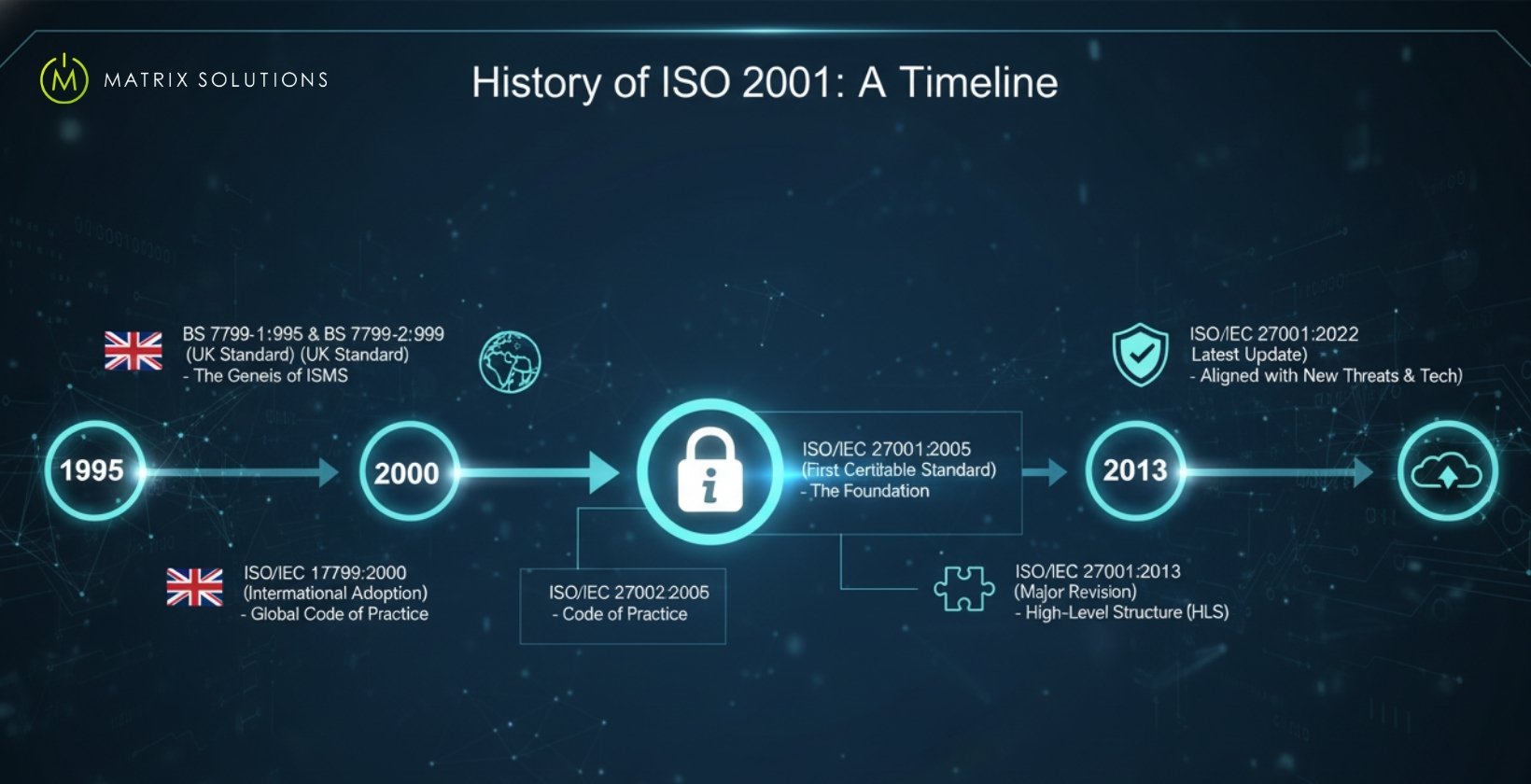
The history of ISO/IEC 27001 begins with its origins in the United Kingdom, where its precursor standard was first developed.
Here’s a timeline of its development:
1. Origin and Early Development (BS 7799)
The origin of ISO 27001 traces to BS 7799, published by the British Standards Institution (BSI Group) in 1995. Back then, the UK Department of Trade and Industry (DTI) guided its development: calling it “Information Technology – Code of Practice for Information Security Management” (BS 7799-1:1995).
The development progressed in two parts:
Part 1 – Code of Practice: A set of best-practice guidelines for managing information security.
Part 2 – Specification for ISMS: BSI introduced BS 7799-2:1999, which set out the formal requirements for an Information Security Management System (ISMS) that could be independently audited and certified.
2. International Adoption and ISO/IEC 17799 (2000)
The success of BS 7799-1 led to its adoption by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
In 2000, BS 7799-1 was published internationally as ISO/IEC 17799:2000, marking its transition from a national guideline to a globally recognised standard for information security management.
3. The Birth of ISO 27001 (2005):
The second part of BS 7799 soon followed the same process. In 2005, the updated form of BS 7799 became ISO/IEC 27001:2005. This release set up a globally recognised certification framework for ISMS.
At the same time, ISO/IEC 17799 was updated as ISO/IEC 27002:2005, establishing the “ISO 27000 series” of standards. While ISO 27001 laid out how things should be organised, ISO 27002 showed how to actually put those ideas into action. Because of that link, both turned into a go-to model for managing data safety.
4. Revisions and Updates
ISO/IEC 27001 has undergone significant revisions since its initial 2005 publication:
1. ISO/IEC 27001:2013 – Back in 2013, ISO/IEC 27001 got a big update.
This revision aligned information security management with other ISO systems through the High-Level Structure (Annex SL). This structure made it easier for organisations to integrate ISO 27001 with different frameworks, such as ISO 9001 (quality) and ISO 14001 (environmental management). Annex A was also refined to better align with ISO/IEC 27002, providing clearer implementation guidance.
2. ISO/IEC 27001:2022 (Current Version)
Released in October 2022, this version modernised the standard for cloud computing and digital transformation. While the core ISMS principles remain, Annex A was fully revised: the number of controls was reduced from 114 to 93 and grouped into four categories: Organisational, People, Physical, and Technological. New controls were added for cloud security, threat intelligence, and data masking.
As of April 30, 2024, certifiers are no longer permitted to issue or renew certificates under the 2013 version – the 2022 update became the current mandatory version.
3. Amendment 1:2024 – Security Meets Sustainability
The newest version, called Amendment 1:2024, focuses on tackling climate issues. Instead of treating them separately, it links data protection, online safety, and personal info handling with eco-friendly efforts. Why? So companies can match their security steps with green promises alongside broader climate targets.
About The ISO/IEC 27001
The ISO/IEC 27000-series, or ‘ISMS Family of Standards,’ is a set of information security standards published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
The series focuses on how to manage information risks and security controls through an overall Information Security Management System (ISMS)–a system similar in design to the management systems for quality assurance (ISO 9000 series), environmental protection (ISO 14000 series), etc.
The series addresses all aspects of information protection, including privacy, confidentiality, cybersecurity, and technical controls. All organisations are encouraged to assess their information risks and treat them (typically using information security controls) according to their needs, using relevant guidance and suggestions.
The ISMS concept adapts to changes in threats, vulnerabilities, and impacts of incidents by incorporating continuous feedback and improvement activities.
The standards come from ISO/IEC JTC1 (Joint Technical Committee 1) SC27 (Subcommittee 27), an international body that meets twice yearly.

What is the Purpose of ISO/IEC 27001?
The main purpose of ISO/IEC 27001 is to give organisations a clear, structured way to manage and protect their information. It sets out how to build an Information Security Management System (ISMS) that keeps data safe, reduces risks, and builds trust.
At its core, ISO 27001 helps organisations:
- Keep data secure by maintaining its confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
- Identify threats, assess vulnerabilities, and apply practical controls to reduce risks.
- Support adherence to laws and regulations such as GDPR and national privacy acts.
- Prepare for incidents and recover quickly from disruptions.
In short, ISO 27001 provides a globally recognised framework for managing information security in a consistent, measurable, and trustworthy way.
Why is the ISO 27001 Standard Important?
ISO/IEC 27001 is a globally recognised standard that helps organisations protect sensitive data, build trust, and maintain compliance through a risk-based ISMS integrating people, processes, and technology.
Does ISO 27001 Cover Cybersecurity?
Yes. The 2022 update of ISO/IEC 27001 adds “cybersecurity” to its title, confirming its role in managing cyber threats. It does so through an ISMS framework focused on identifying, reducing, and continuously improving security across all areas.
The updated Annex A controls, aligned with ISO/IEC 27002, strengthen this connection with specific cyber-focused measures, including:
- A.5.7: Threat intelligence: establishing processes to collect and analyse threat data.
- A.5.30: ICT readiness for business continuity: ensuring systems can recover quickly after cyber incidents.
- A.8.9: Configuration management: preventing vulnerabilities through secure system configurations.
- A.8.16: Monitoring activities: detecting, analysing, and responding to suspicious activity.
- A.8.28: Secure coding: reducing software-based vulnerabilities
Implementing these controls helps prevent threats like phishing, ransomware, and data theft. The 2022 update also aligns well with frameworks endorsed by the Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC), helping organisations strengthen resilience against modern cyber threats and maintain compliance with national cybersecurity expectations.
Does ISO 27001 Cover Data Privacy?
Yes. ISO 27001 explicitly includes “privacy protection” in its title, recognising that safeguarding personal information is a critical part of modern information security. The standard ensures that organisations handling personally identifiable information (PII) apply appropriate controls to prevent misuse, unauthorised access, or data loss.
Privacy-related requirements appear directly in Annex A, most notably:
- A.5.34: Defines privacy and PII protection requirements.
- A.5.15–A.5.18: Establish access control policies for handling personal data.
- A.8.10–A.8.11: Ensure secure data deletion and masking when no longer needed.
While ISO 27001 provides the foundation for data security, many organisations also adopt ISO/IEC 27701, which extends it into a Privacy Information Management System (PIMS). This addition offers clearer guidance for meeting privacy laws such as the Australian Privacy Act 1988, regulated by the Office of the Australian Information Commissioner (OAIC), as well as international frameworks like GDPR and CCPA.
For Matrix Solutions and its legal clients, these controls ensure sensitive data is protected at every stage, from document creation to storage and deletion, maintaining compliance and client trust.
What Does it Mean to be ISO Certified?

Being ISO 27001 certified means an accredited certification body has verified that your organisation’s Information Security Management System (ISMS) meets all requirements of the ISO/IEC 27001 standard.
To achieve certification, organisations must establish and document an ISMS, identify and manage information-security risks, implement relevant Annex A controls, and undergo external audits with periodic reviews.
Although voluntary, ISO 27001 certification is globally recognised. It demonstrates a strong commitment to data protection, compliance, and client trust, particularly valuable for law firms and professional service providers handling sensitive information.
How Does ISO 27001 Work?
ISO 27001 works by creating a structured management system that protects information assets through ongoing risk assessment and control.
It requires organisations to:
- Assess security risks by identifying threats and vulnerabilities.
- Apply technical, physical, and organisational controls to manage unacceptable risks.
- Monitor and improve their ISMS using the Plan–Do–Check–Act (PDCA) cycle.
Supporting standards like ISO 27001 and ISO/IEC 27005 provide detailed guidance. In practice, ISO 27001 turns security into a proactive, measurable, and business-aligned process rather than a reactive one.
What are the ISO 27001 Requirements and Compliance Obligations?
To achieve and maintain ISO 27001 certification, an organisation must implement a documented Information Security Management System (ISMS) that meets the standard’s structural and operational requirements while ensuring ongoing compliance.
The core requirements under Clauses 4–10 include:
- Context: Identify internal and external factors and stakeholders affecting security.
- Leadership: Assign roles and ensure top management accountability.
- Planning: Assess risks, define treatment plans, and set ISMS objectives.
- Support: Provide resources, training, and documentation.
- Operation: Implement and manage ISMS processes.
- Evaluation: Audit and review performance.
- Improvement: Apply corrective actions and continuous improvement.
Organisations must also apply 93 Annex A controls across four categories: Organisational, People, Physical, and Technological, to mitigate security risks.
Ongoing compliance requires continuous monitoring, internal audits, and management reviews to ensure the ISMS remains effective, secure, and aligned with evolving threats and regulations.
What are the Three Principles of ISO 27001?
ISO/IEC 27001 is built on three core principles that define how information must be protected within an organisation. Together, these principles form the foundation of every Information Security Management System (ISMS):
1. Confidentiality: Information must be accessible only to authorised individuals, preventing unauthorised disclosure or data leaks.
2. Integrity: Information must remain accurate, complete, and reliable, ensuring that data and systems are not improperly modified.
3. Availability: Authorised users must have access to information and systems whenever needed, supporting business continuity and client trust.
These principles guide how organisations assess risk, apply controls, and ensure information remains secure and reliable.
What are the New Four Categories of ISO/IEC 27001?
The 2022 revision of ISO 27001 reorganised its control set in Annex A to align with ISO/IEC 27002, reducing the number of controls from 114 to 93.
Annex A Section | Category | Control Unit | Focus and Examples |
A.5 – Organisational Controls | 37 | Define governance, policies, and processes that guide how information security is managed. | Includes policies on access control, supplier relationships, asset management, information classification, and risk assessment frameworks. |
A.6 – People Controls | 8 | Address human factors in information security, ensuring personnel understand and fulfil their security responsibilities. | Examples: security awareness and training, background verification, and clearly defined roles and responsibilities. |
A.7 – Physical Controls | 14 | Protect physical environments, facilities, and assets from unauthorised access, damage, or interference. | Includes secure areas, entry controls, CCTV, equipment protection, and physical security monitoring. |
A.8 – Technological Controls | 34 | Focus on technical safeguards that secure data and systems across software, hardware, and network environments. | Examples: encryption, backup, secure configuration, malware protection, data deletion, and system monitoring. |
This streamlined structure simplifies implementation and aligns ISO 27001 with global frameworks such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework and Zero Trust Architecture.
What are the ISO 27001 Controls?

ISO 27001 controls, detailed in Annex A, are technical, physical, and organisational safeguards designed to reduce information-security risks.
- Access control and encryption to prevent unauthorised access
- Cloud and supplier management to secure third parties
- Physical security for offices and equipment
- Incident response and backups for continuity
Organisations tailor these controls to their risk profile, maintaining confidentiality, integrity, and availability through regular review and updates.
What is the Difference Between ISO 27001 and ISMS?
ISO 27001 is the international standard that defines how to establish and maintain an Information Security Management System (ISMS).
An ISMS is the practical framework, your organisation’s policies, procedures, and controls for managing information security risks.
ISO 27001 outlines what to achieve, while the ISMS details how it’s done.
Who Needs ISO 27001 Certification?
ISO 27001 certification benefits any organisation managing sensitive or regulated data, including law firms, financial institutions, healthcare providers, technology companies, and government contractors.
Certification shows that an organisation effectively manages information security risks, building trust and credibility by protecting client data to international standards.
Importance of ISO 27001 for Law Firms
Law firms handle highly sensitive information, from client records and case files to financial and corporate data. In today’s digital environment, even a minor breach can lead to regulatory penalties and loss of client confidence.
ISO 27001 certification helps law firms:
- Protect client confidentiality through risk-based controls.
- Comply with privacy laws such as the Australian Privacy Act 1988 and GDPR.
- Maintain business continuity and strengthen client confidence.
For many clients, ISO 27001 certification is now expected, proving a firm values information security as much as its legal duties.
How Can Matrix Solutions Help?
Matrix Solutions helps law firms and professional-service organisations implement and maintain ISO 27001-compliant Information Security Management Systems. We provide end-to-end support, from initial gap assessments to long-term compliance management, combining more than 20 years of IT and legal-sector expertise to make certification practical and sustainable.
Questions Regarding ISO 27001
Is ISO 27001 mandatory?
No, ISO 27001 is not legally mandatory, but many industries and clients require it to prove effective information-security management and compliance with privacy laws.
Can small businesses get certified for ISO 27001?
Yes. ISO 27001 applies to organisations of all sizes. Certification helps small businesses show credibility, improve security, and meet client or supplier expectations.
Are there any ongoing requirements after achieving ISO 27001 certification?
Yes. Certified organisations must perform internal audits, management reviews, and continuous improvements to maintain compliance during surveillance audits.
What is the latest ISO 27001 standard?
The latest version is ISO/IEC 27001:2022, updated to align with ISO/IEC 27002:2022 and reflect new controls for cloud security and digital risks.
Can multiple sites or divisions within an organisation be certified under one ISO 27001 certification?
Yes. A multi-site certification is possible if all sites operate under the same ISMS and are included in the audit scope.
Is ISO 27001 better than Cyber Essentials?
ISO 27001 is broader and internationally recognised, covering full ISMS implementation. Cyber Essentials is UK-specific and focuses mainly on basic cybersecurity controls.
Can ISO 27001 certification be used as evidence for GDPR compliance?
Yes. ISO 27001 supports GDPR compliance by providing structured data protection and risk management, though it doesn’t replace legal obligations under GDPR.
What’s the difference between ISO 27001 and 27002?
ISO 27001 defines ISMS requirements, while ISO 27002 provides detailed guidance on implementing its security controls.
Are ISO 27001 and PCI DSS compatible?
Yes. Both promote secure data management. ISO 27001 provides a framework for overall security, while PCI DSS focuses specifically on payment-card data protection.
Can ISO 27001 certification be used for government contracts?
Yes. Many government tenders and suppliers require ISO 27001 certification as proof of robust information-security management.
What is the difference between ISO 27000 and 27001?
ISO 27000 defines the ISMS vocabulary and overview. ISO 27001 specifies the actual requirements for implementing and certifying an ISMS.
Can a company achieve ISO 27001 certification without hiring a consultant?
Yes, but hiring experts simplifies the process. Consultants help with documentation, risk assessments, and audit readiness.
Is ISO 27001 a legal requirement?
Not directly. However, certification helps organisations comply with laws like the Australian Privacy Act 1988 and GDPR by demonstrating data protection measures.
Conclusion
ISO/IEC 27001 remains the benchmark for information-security management, helping organisations protect data, meet regulations, and earn client trust. With more than two decades of experience, Matrix Solutions empowers firms to build ISO 27001-aligned systems. Our team provides practical, end-to-end support for lasting compliance and security.
Let’s work together to safeguard your business security standards!
Ready to secure your organisation’s future with ISO 27001 certification?
Contact Matrix Solutions today to get expert guidance on building and maintaining a robust Information Security Management System (ISMS) that ensures compliance, protects sensitive data, and strengthens client trust.
Contact Now



