In September 2025, Cloudflare blocked the largest-ever DDoS attack, peaking at 11.5 terabits per second and powered by hijacked IoT and cloud systems. It’s a clear reminder that today’s cyber threats are evolving faster, hitting harder, and growing more complex than ever!
Network security threats are a serious concern in today’s digital world. Cybercriminals are finding new ways to target businesses, risking sensitive data, daily operations, and reputations. Ignoring these threats can lead to costly consequences, making prevention a top priority.
To protect your organisation, it’s crucial to understand network security threats and how they can affect your business. By recognising risks and adopting strong protection strategies, you can stay secure and build trust with your customers. Whether you run a small or large business, staying prepared is more essential now than ever.
The Basics of Network Security
In today’s digital-first world, network security is the backbone of every business’s operations. It safeguards sensitive data, ensures the smooth functioning of systems, and protects against the rising tide of cyberattacks. Businesses risk financial losses, damaged reputations, and operational disruptions without robust security measures. Understanding network security threats is the first step toward building a solid defence strategy – a cornerstone of modern managed IT services – which we’ll explore further in the sections below.
What is Network Security?
Network security is a fundamental and crucial part of an organisation’s IT infrastructure environment. Network security protects computer networks from cyberattacks, unauthorised access, and data breaches. Its primary objective is to safeguard sensitive information and maintain uninterrupted business operations by implementing robust protective measures and sophisticated technologies.
What are Network Security Threats?
Network security threats are potential vulnerabilities, weaknesses, and risks within network infrastructure that malicious actors can exploit. The common network security threats span malicious software, deception tactics targeting users, physical network disruption, and exploiting systemic vulnerabilities. These threats aim to compromise the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information across a network.
How Network Security Threats Impact Your Business
Network security threats can have far-reaching effects on your business, impacting more than just IT systems.
- Financial Losses: Cyberattacks may lead to stolen funds, ransom payments, or expensive downtime. Recovering from these can drain resources meant for growth.
- Operational Disruption: Ransomware and similar threats can disrupt essential business operations, causing project delays and diminishing customer satisfaction.
- Reputational Damage: A data breach can undermine customer trust, damage your brand’s reputation, and result in lost clients and sales.
- Compliance Penalties: Failing to secure your network can result in fines for violating data protection laws, especially in sectors like finance and healthcare.
Common Types of Network Security Threats

Understanding the threats targeting your network is crucial for creating an effective defence. Network threats can be broadly classified into software-based, human-based, and infrastructure-based risks. From malicious software to sophisticated social engineering tactics, each threat type poses unique challenges that businesses must address.
Malware (Viruses, Worms, Ransomware, and Trojans)
Malware is malicious software designed to harm networks, devices, or users. Here are some of the malware:
- Viruses: Attach themselves to files or programs and spread when opened, damaging systems.
- Worms: Self-replicating programs that spread across networks, often consuming bandwidth and resources.
- Ransomware: Encrypts data and demands payment for its release, halting business operations.
- Trojans: Disguise as legitimate software, tricking users into downloading and giving attackers access to networks.
These types of malware can lead to data theft, financial losses, and operational downtime.
Phishing and Social Engineering Attacks
Phishing and social engineering attacks exploit human behaviour to compromise networks.
- Email Phishing: Fraudulent emails trick users into sharing sensitive information.
- Spear Phishing: Targeted phishing attacks customised for specific individuals or organisations.
- Whaling: High-level phishing attacks focused on executives to cause significant harm.
- Social Engineering: Manipulates trust and creates a false sense of urgency to gain unauthorised access to networks.
Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks
DDoS attacks overwhelm networks or servers with excessive traffic, causing downtime and disrupting operations. This prevents legitimate users from accessing services, leading to revenue loss and reputational damage. Implementing traffic filtering and load balancing measures helps businesses protect against these attacks and maintain continuity.
Insider Threats
Insider threats come from within an organisation and can be intentional or accidental.
- Malicious Insiders: Employees or contractors who intentionally misuse access to harm the organisation.
- Negligent Insiders: Users who unintentionally compromise security by ignoring protocols or falling victim to phishing.
Businesses can mitigate insider threats by implementing strict access controls, employee training, and regular security audits.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
MitM attacks occur when an attacker intercepts communications between two parties without their knowledge. These attacks can compromise sensitive data, such as login credentials or financial information, leading to identity theft or fraud. Common methods include unsecured Wi-Fi and spoofed websites.
Data Breaches and Loss
Data breaches happen when attackers gain unauthorised access to systems, often due to:
- Misconfigurations of security settings.
- Phishing attacks trick users into revealing information.
- Lack of encryption makes data vulnerable in transit or storage.
- Data breaches can leak sensitive information, result in legal repercussions, and cause significant financial losses.
Evolution of Network Security Threats

As technology advances, so do the threats that target it. Cybercriminals are becoming smarter, using new tools like AI, automation, and social engineering to exploit weaknesses across cloud platforms, IoT networks, and remote work setups. Businesses can no longer rely on traditional perimeter firewalls alone — they need layered, adaptive, and intelligent security frameworks that evolve with the threat landscape.
Evolution Timeline of Network Threats
Era | Key Threats | Focus of Defence |
1980s–1990s | Early viruses and worms like Brain and Morris Worm | Basic antivirus software and protecting individual computers |
Late 1990s–2000s | DoS and DDoS attacks, web vulnerabilities (SQL injection, XSS) | Firewalls and intrusion detection to protect servers and websites |
Mid-2000s–2010s | Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs), phishing, botnets, mobile malware | Data protection, threat intelligence, behavioural monitoring |
2010s–Present | Ransomware, supply chain attacks, cloud and IoT risks, AI-powered threats | Zero Trust security, continuous monitoring, AI-based defence tools |
Modern Network Threat: New Challenges
Today’s network security environment looks very different from even a few years ago and modern network threats are no longer limited to viruses or simple hacks. Cybercriminals now combine traditional methods with advanced, technology-driven attacks to launch faster, more convincing, and more coordinated attacks.
Businesses now face a broad mix of network threats. Ransomware, phishing, and DDoS attacks remain constant dangers, but new challenges have emerged like AI-powered cyberattacks, supply chain compromises, and weaknesses across cloud and IoT environments. The scale, speed, and precision of these threats make modern cybercrime harder to detect, defend against, and recover from.
Emerging Threats and Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) are long-term, targeted attacks in which cybercriminals gain unauthorised access to a network and remain undetected for extended periods. They don’t cause immediate disruption; instead, they gather intelligence, steal sensitive data, or manipulate systems from the inside.
Modern APTs are more sophisticated than ever. Attackers now use AI-generated phishing, zero-day exploits, and supply chain vulnerabilities to reach their targets. Ransomware has also evolved into double and triple extortion schemes, where stolen data is not only encrypted but also threatened with public exposure. These persistent threats demand ongoing monitoring, rapid detection, and a proactive security culture.
The Impact of IoT on Network Security
The rise of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has increased network security attacks. Every connected camera, sensor, or smart device can become an entry point for attackers. Many IoT devices are poorly secured, creating vulnerabilities that attackers exploit.
Once compromised, these devices can be used to spy, steal data, or launch large-scale attacks. The record-breaking 11.5 Tbps DDoS attack blocked by Cloudflare in 2025 showed how hijacked IoT and cloud systems can flood global networks within minutes. As IoT adoption grows, securing these endpoints has become one of the biggest challenges in modern network defence.
Threats from Cloud Computing and Remote Work Environments
Cloud computing and remote work environments reshaped how businesses operate but they also present unique security challenges. Misconfigured cloud settings, unsecured APIs, and weak access controls often give attackers an easy path inside. Once they’re in, they can move laterally between systems, gaining access to critical data.
Remote work adds another layer of complexity. Employees using personal devices or connecting through public Wi-Fi increase the risk of data leaks and unauthorised access. In many cases, insider threats, whether accidental or deliberate, contribute to breaches.
To stay protected, organisations need to strengthen their cloud security posture through Zero Trust access controls, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and end-to-end encryption. Continuous visibility and monitoring across cloud and remote environments are no longer optional — they’re essential.
Best Practices for Mitigating Network Security Threats

Prevention is also better than a cure. So, taking proactive steps helps minimise network security threats, keeping your business safe. You can prevent breaches and protect sensitive data by implementing the practices mentioned below.
Implementing Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are crucial for blocking unauthorised access and detecting suspicious activities. Firewalls filter incoming and outgoing traffic to prevent harmful data from entering.
IDS monitors network activity in real time, alerting administrators to unusual behaviour or potential threats. Together, they provide a strong defence against different types of cyberattacks.
Regular Software and Security Updates
Organisations must ensure all software and systems are up-to-date with the latest security patches to close vulnerabilities that attackers might exploit. Keeping software updated is vital for closing security vulnerabilities, as many cyber-attacks exploit outdated software.
Strong Authentication and Access Control
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and strict access control are key to securing your network. MFA adds extra protection by requiring multiple forms of identification, making it harder for unauthorised users to gain access. Access control ensures that only authorised individuals can access sensitive data, reducing the risk of internal and external threats.
Employee Education and Awareness Programs
Providing regular training helps employees recognize phishing attempts, manage passwords securely, and follow cybersecurity protocols to reduce human error. Employee training and awareness are essential to mitigating network threats, considering that 95% of cybersecurity breaches are caused by human error.
Encryption and Data Protection
Encryption is essential for protecting sensitive data. By converting data into unreadable code, encryption ensures that even if it is intercepted, it cannot be accessed without the proper decryption key. Encrypting data—whether stored or in transit—adds an extra layer of security, helping you comply with regulations and protect customer information.
Tools and Solutions for Network Security Threat Prevention
Network security threat prevention relies on implementing a multi-layered defense strategy using a combination of technical tools, management systems, and strategic processes. The right solutions help identify vulnerabilities, detect suspicious activity, and neutralise threats.
1. Antivirus and Anti-malware Software
Antivirus software tools are essential for detecting, preventing, and removing malicious software like viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, and spyware from endpoints and servers.
- Signature-based detection: Identifies known malware by comparing files to a database of malware signatures.
- Heuristic-based detection: Analyzes code for suspicious behavior that might indicate new or unknown malware.
- Behavioral analysis: Monitors programs for malicious actions regardless of their signature.
2. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
EDR tools continuously monitor and collect data from endpoint devices (laptops, desktops, servers) to detect and investigate suspicious activities. They provide advanced threat detection, incident response capabilities, and forensic analysis.
3. Network Security Monitoring Solutions
Real-time network security monitoring solutions are vital for detecting abnormalities and preventing breaches. These tools monitor network traffic, looking for unusual patterns or behaviour.
By identifying suspicious activity early, you can immediately mitigate threats before they escalate.
4. Vulnerability Scanning and Penetration Testing
Vulnerability scanning and penetration testing are critical for identifying and addressing weaknesses in a network before attackers can exploit them. Vulnerability scanners systematically check for known security flaws.
At the same time, penetration testing simulates real-world attacks to test the network’s defence mechanisms. These proactive measures help businesses patch vulnerabilities and strengthen their security posture.
Partnering with Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs)
Outsourcing to MSSPs offers businesses better protection through expert-managed solutions. MSSPs provide 24/7 monitoring, threat detection, and response.
By partnering with an MSSP, you can access advanced security technologies and skilled professionals without an in-house security team.
Steps to Strengthen Network Security
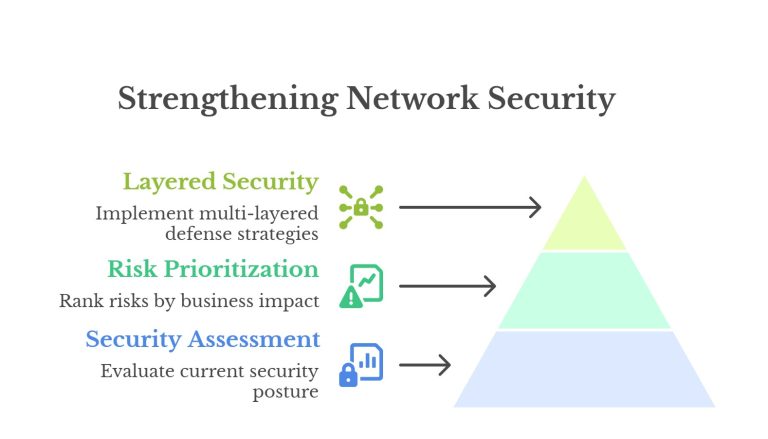
Enhancing network security requires a systematic approach for SMEs. By following the steps mentioned below, you can build robust network security.
1. Assessing Your Current Security Posture
The first step in strengthening your network security is evaluating your current measures. Identify existing security protocols, tools, and systems and assess their effectiveness. Regularly audit your network to uncover potential gaps, outdated software, and weaknesses that attackers could exploit.
2. Prioritising Risks Based on Business Needs
Once you’ve identified vulnerabilities, it’s important to prioritise them based on their impact on your business. Focus on addressing the most critical risks with significant financial, operational, or reputational consequences. This approach ensures your resources are focused on protecting what matters most to your organisation.
3. Implementing Layered Security Strategies
A layered security approach helps protect your network from multiple attacks. A combination of security measures creates barriers that make it harder to penetrate your systems. This layered approach adds depth to your security, reducing the chances of a successful attack.
The Future of Network Security: Anticipating New Threats

Network security constantly evolves as new technologies emerge and threats become more dangerous. To stay protected, businesses must prepare for future challenges by understanding trends and embracing innovative solutions.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Security
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) transform network security by enhancing threat detection and response. These technologies can analyse vast amounts of data to identify patterns, detect abnormalities, and predict potential attacks faster.
How Businesses Can Stay Ahead of New Threats
Staying ahead of emerging threats requires proactive measures. Businesses should prioritise ongoing staff education, regularly updating employees on new security practices and potential risks. Adopting cutting-edge tools like advanced threat monitoring systems can improve defence systems.
Additionally, partnering with cybersecurity experts ensures access to the latest knowledge and strategies, helping organisations adapt to the ever-changing threat landscape.
FAQs: Network Security Threats
What is the difference between cyber threats and network security threats?
Cyber threats are any malicious activity targeting computer systems, data, or networks, encompassing many risks like phishing, malware, and ransomware. On the other hand, network security threats specifically target vulnerabilities within a network infrastructure, such as unauthorised access, data interception, or denial-of-service attacks.
How do cloud services impact network security?
Cloud services impact network security by introducing new vulnerabilities, such as unsecured data transfers, misconfigured servers, and shared resources.
What role do VPNs play in protecting against network threats?
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) encrypt internet connections, providing a secure channel for data transmission and protecting sensitive information.
How can small businesses protect against network security threats?
Small businesses can protect against threats by implementing basic security measures like firewalls, antivirus software, and regular updates. Educating employees, adopting strong passwords, and enabling multi-factor authentication strengthen defences.
What is the role of artificial intelligence in combating network security threats?
AI enhances network security by detecting anomalies, predicting threats, and automating responses. AI-powered systems can analyse vast amounts of data in real-time to identify suspicious activity, enabling businesses to act quickly and effectively against potential breaches.
What are the latest trends in network security threats?
The latest trends in network security threats are characterised by attackers’ increasing reliance on sophisticated Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools and the expansion of the attack surface due to modern enterprise architectures. These threats include AI-driven attacks, double-extortion ransomware, zero-day exploits, and growing risks from cloud, IoT, and supply chain vulnerabilities.
Conclusion: Staying Ahead of Network Security Threats
Staying ahead of network security threats requires constant vigilance and proactive measures. Businesses can significantly reduce risk by understanding the nature of evolving threats, implementing robust security strategies, and adopting advanced tools.
Partnering with experts can make all the difference to protect your organisation. Matrix Solutions offers comprehensive Managed IT Security Services to safeguard your business against emerging security threats. With our expertise in network monitoring, threat prevention, and customised IT solutions in Sydney, Brisbane, or across Australia, we help businesses stay one step ahead.
Don't wait for a breach!
Stay protected from the next big cyber threat
Cyber threats aren’t slowing down — but your business can stay ahead of them. With Matrix Solutions’ expert-managed IT and cybersecurity services, you get constant protection, smarter monitoring, and peace of mind.
Let’s secure your network today!



