A hybrid cloud strategy allows Australian firms to run workloads across public and on-premises systems while maintaining control over sensitive data. It has become the preferred model for legal, financial, and insurance SMEs that require both agility and regulatory compliance.
To deliver measurable business value, your strategy must align with security, governance, and long-term operational goals. At Matrix Solutions, we support organisations in achieving this alignment through proven hybrid models.
What Is a Hybrid Cloud Strategy?
A hybrid cloud strategy connects public cloud platforms with private or on-prem systems. Unlike a public cloud, where all workloads run off-site, or a private setup, where each workload belongs. This provides more control without sacrificing access to cloud scalability.
The hybrid approach helps businesses separate critical data from general operations. For example, a law firm might store case files privately while using cloud-based document tools for collaboration. This balance supports compliance, reduces costs, and helps SMEs grow without compromising governance or performance.
Why SMEs Need a Hybrid Cloud Strategy
SMEs in legal, finance, and insurance face tight IT budgets, strict data regulations, and increasing digital demands. Fully relying on the public cloud can introduce security risks, while sticking to private infrastructure limits flexibility and strains internal resources, especially when managing workloads across multiple locations or teams.
A hybrid cloud strategy gives firms control over sensitive data while using public cloud services for scale and cost efficiency. For example, a financial firm might store client records on-premises but run analytics in the cloud. This enables smarter growth, stronger compliance, and adaptable systems that evolve with the business.
Key Components of a Hybrid Cloud Strategy
A successful hybrid cloud strategy relies on four foundational components. Each plays a critical role in connecting systems, enforcing control, and enabling secure scalability. Together, they form the framework that supports performance, compliance, and business continuity.
Here are the essential parts every SME needs to get right.
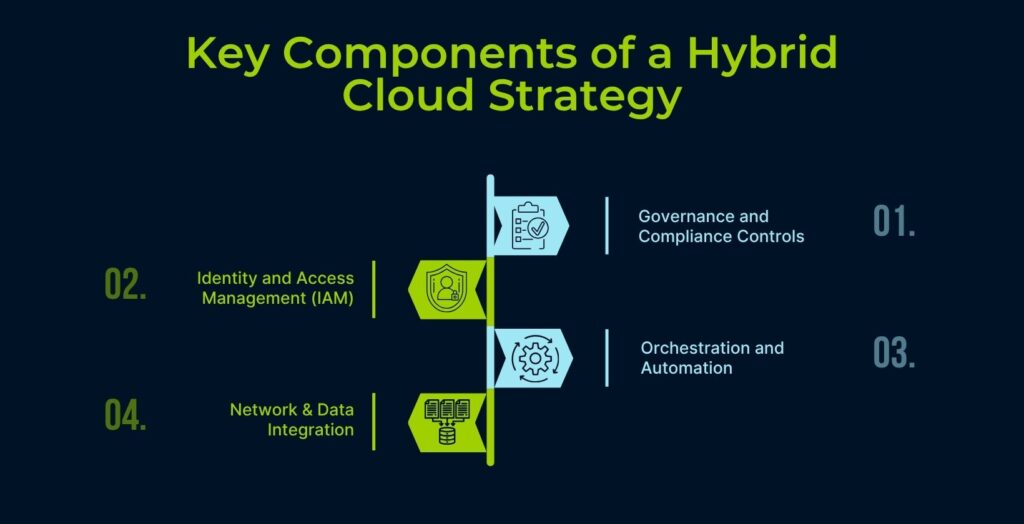
I. Governance and Compliance Controls
Effective governance keeps hybrid cloud environments accountable and audit-ready. For law firms and financial organisations, this means setting clear data handling rules, enforcing access controls, and maintaining an audit trail. These practices support compliance with standards such as ISO 27001 and APRA CPS 234, ensuring legal and security expectations are met.
II. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Cloud IAM defines who can access what and from where. In hybrid environments, it maintains secure workflows between public and private systems. For example, a law firm might keep client files private while enabling collaboration through cloud tools, preserving compliance and improving usability.
III. Orchestration and Automation
Cloud orchestration tools, such as Kubernetes and Terraform, automate deployment, scaling, and workload movement. This reduces manual effort, enforces consistent policies, and improves responsiveness to demand or risk. SMEs benefit through time savings, reduced errors, and a more reliable way to maintain compliance.
IV. Network & Data Integration
Hybrid cloud relies on a secure network and data integration between on-premises and cloud platforms. APIs handle connectivity, while low-latency frameworks support real-time syncing. This is especially important in finance and legal sectors, where even minor data delays can impact compliance, accuracy, or client service.
How to Build a Successful Hybrid Cloud Strategy
A well-executed hybrid cloud implementation starts with clear planning and ends with secure, scalable systems. Below are eight practical steps every SME should follow to ensure success.
- Assess your infrastructure: Map existing systems, legacy applications, and cloud dependencies across departments.
- Classify data by sensitivity: Identify which data must remain on-premises for compliance and which workloads can move to the cloud.
- Choose compatible cloud platforms: Select providers that offer interoperability, local data hosting, and cost-effective scalability.
- Define governance policies early: Set rules for access control, data protection, and regulatory compliance across all environments.
- Apply IAM and security controls: Implement consistent identity and access policies across both private and public systems.
- Run pilot deployments: Test low-risk workloads to validate performance, connectivity, and policy enforcement.
- Automate workload orchestration: Use tools like Kubernetes or Terraform to manage scaling, updates, and failover with minimal manual effort.
- Monitor, optimise, and expand: Track performance, review usage, and adjust configurations to support growth and minimise risk.
Benefits of a Hybrid Cloud Strategy
A well-structured hybrid cloud strategy gives regulated industries clear advantages across compliance, flexibility, cost, and continuity. Below are five key benefits for firms managing sensitive data.
1. Regulatory Compliance
A hybrid cloud strategy enables law firms to meet strict data handling requirements. Law firms and financial institutions can keep sensitive records in on-premises systems, complying with frameworks like APRA CPS 234 and the Privacy Act, while using the cloud for less regulated workloads.
2. Operational Flexibility
Workloads shift between private and public environments based on real-time business needs. A legal team may run its case management platform in-house while using cloud tools for secure client collaboration, enabling responsiveness without loss of control.
3. Cost Efficiency
Hybrid models reduce hardware and infrastructure costs by offloading non-sensitive tasks to the cloud. For example, a financial services provider might host customer portals in the cloud while keeping transaction systems local, scaling without overinvesting in private infrastructure.
4. Disaster Recovery
Hybrid setups enable faster recovery using off-site backups and cloud redundancy. A law firm can replicate critical files to a secure cloud region, ensuring uninterrupted access during system failure or local disruption.
5. Business Continuity
Hybrid systems maintain service during outages or cyber threats by failing over to cloud-hosted applications. This is essential for financial and legal teams managing time-sensitive operations and client commitments.
Also, learn about the benefits of Managed IT services for small businesses!
Hybrid Cloud vs Multi-Cloud: Strategic Differences
Many businesses confuse hybrid and multi-cloud models, but they serve different purposes. Understanding the difference is essential when designing cloud architecture that meets compliance, performance, or risk management goals.

When to Use Which
Hybrid cloud solutions are ideal for regulation-heavy industries where control over sensitive data is critical. Multi-cloud is better suited to businesses prioritising uptime, geographic redundancy, or vendor diversification. The right model depends on whether compliance or availability drives your infrastructure strategy.
Pros and Cons Comparison Table
| Criteria | Hybrid Cloud | Multi-cloud |
| Cost | Cost-effective for compliance; fixed costs from private infrastructure | Flexible pricing across vendors; hidden costs from integration & redundancy |
| Complexity | Higher due to the integration of on-prem and cloud systems | Complex to manage across 3roviders, platforms, & service-level agreements (SLAs) |
| Control | High control over sensitive data and governance | Moderate control; shared across multiple vendor systems |
| Performance | Strong for latency-sensitive workloads hosted locally | Optimised for uptime and global service availability |
Interoperability and Vendor Lock-in Risks
Hybrid cloud reduces vendor lock-in by keeping critical systems on-premises, but proprietary tools can still create dependencies. To avoid this, SMEs should use open APIs, containerised apps, and orchestration tools that support cross-platform compatibility.
Common Challenges in Hybrid Cloud Implementation
Hybrid cloud offers flexibility and control, but implementation isn’t without friction. Key issues range from orchestration complexity to skills shortages, all of which can affect compliance, cost, and system stability if not addressed early.
I. Complexity in Orchestration
Coordinating workloads across hybrid systems introduces technical friction. Tools like Kubernetes, Ansible, and Terraform often come with conflicting configurations and version requirements. Without standardised processes, syncing deployments and enforcing policies across environments slows delivery and increases compliance risk. SMEs need consistent orchestration workflows to avoid integration delays.
II. Security and Identity Management
Fragmented identity systems and inconsistent data controls are leading security risks in hybrid setups. IAM misconfigurations may expose sensitive workloads across cloud and on-prem environments. Strong governance frameworks and zero-trust access models, supported by continuous endpoint monitoring, are essential for reducing lateral threats and protecting data.
III. Skillset Gaps in IT Teams
Most internal IT teams lack hybrid cloud-specific expertise. SMEs often struggle with container orchestration, hybrid IAM, and policy automation. Upskilling through certifications or working with a managed IT partner can help close the knowledge gap and reduce deployment risks.
IV. Cost Mismanagement
Hybrid environments often suffer from limited cost visibility. Without cost tagging, real-time tracking, and usage alerts, SMEs risk overspending on idle or duplicate resources. Automated billing and usage analytics help finance teams regain control and align budgets with actual business needs.
Partnering with a Managed IT Provider
Managed IT service providers simplify hybrid adoption by handling deployment, governance, and ongoing management. They bring experience in cloud tools, security frameworks, and compliance workflows. At Matrix Solutions, we help legal and finance teams maintain secure hybrid environments without overloading internal resources.
Hybrid Cloud Use Cases by Industry
Industries adopt hybrid cloud for different reasons—some need control, others need scale. Real-world examples show how hybrid strategies solve business challenges across the law, finance, and insurance sectors.
Legal Firms: Secure Case File Storage
Law firms use hybrid cloud to secure client data while enabling flexible access. Confidential case files remain in private systems to meet privacy and court-handling obligations. At the same time, cloud-based legal apps streamline e-discovery, remote collaboration, and document management across teams and locations.
Financial Services: Core in Private, BI in Public
Financial institutions use hybrid models to separate sensitive workloads from data-heavy analytics. Core platforms, including transaction ledgers, customer records, and payment gateways, remain on private infrastructure to meet APRA and latency requirements. Public cloud services then support fraud detection, BI dashboards, and AI models, providing secure, real-time insights without shifting critical systems off-premises.
Insurance: Hybrid Claims and CRM Systems
Insurance providers benefit from hybrid cloud by linking internal CRMs with cloud-based claims and policy tools. On-prem systems keep customer data and underwriting logic secure. Meanwhile, cloud-hosted workflows improve claim turnaround, agent collaboration, and automation, reducing infrastructure costs while maintaining compliance with industry standards.
Matrix Solutions: Your Hybrid Cloud Partner
Matrix Solutions is a proven managed cloud solutions provider for Australian firms in the legal, finance, and insurance sectors. We help organisations design hybrid environments that support compliance, data control, and long-term performance, ensuring cloud architecture aligns with local regulatory frameworks and operational needs.
Our team delivers local private cloud hosting, layered security, and ongoing compliance monitoring, tailored to Australian data sovereignty laws.
Request a no-obligation assessment from Matrix Solutions today if your firm needs a secure, scalable hybrid setup.
7 Mistakes Firms Make in Hybrid Cloud Adoption
Many hybrid cloud rollouts fail due to missteps that are entirely preventable. These errors often lead to poor data placement, inflated costs, or compliance gaps. Recognising the most common mistakes is key to avoiding setbacks during implementation.

Mistake 1: Skipping Workload Classification
Failing to classify workloads by sensitivity, performance, and legal need results in misplacement. Critical systems may end up in insecure or inefficient environments, increasing latency and compliance risks. A proper hybrid strategy begins with mapping data to the appropriate environment—public or private—based on risk and regulation.
Mistake 2: Underestimating Integration Complexity
Hybrid cloud integration often breaks down when apps aren’t designed to sync across environments. The result is data silos, system downtime, and reduced performance. Using middleware or API layers early in the architecture phase ensures reliable connectivity and fewer operational issues.
Mistake 3: Misaligned Compliance Planning
Assuming cloud platforms automatically meet regulatory standards leads to costly gaps. Without mapping workloads to frameworks like APRA CPS 234 or the Australian Privacy Principles, firms risk non-compliance. Aligning privacy, residency, and governance rules early helps protect data and reputation.
Mistake 4: Ignoring Vendor Lock-In Risks
Relying on proprietary services without planning for portability can limit future flexibility. In hybrid environments, this reduces scalability and increases dependency. Firms can avoid vendor lock-in by using open standards, containerisation, and orchestration tools that support multi-cloud setups.
Mistake 5: Lack of Cost Governance
Without real-time visibility, hybrid cloud costs quickly spiral. Egress fees, idle resources, and poor usage tracking are common culprits. Applying FinOps principles, tagging workloads, and setting usage alerts helps firms keep spending aligned with actual business needs.
Mistake 6: Failing to Upskill IT Teams
Most SMEs lack hybrid-specific skills in orchestration, compliance, and multi-cloud operations. This causes deployment delays and security risks. Upskilling through certifications or partnering with managed providers like Matrix Solutions helps close the expertise gap.
Mistake 7: No Change Management Plan
Hybrid adoption fails when people resist new tools or processes. Without structured management, teams struggle with rollouts and long-term adoption. Phased implementations, internal champions, and clear documentation support smoother transitions across departments.
FAQs on Hybrid Cloud Strategy
Which cloud migration strategy aligns best with a hybrid cloud deployment?
The cloud migration strategy that aligns best with a hybrid cloud deployment is a phased or workload-based approach. It allows organisations to shift applications while maintaining control over compliance-critical systems on-premise gradually.
Is a hybrid cloud more secure than a public cloud?
Yes, hybrid cloud is more secure than public cloud for regulated industries. It enables isolation of critical workloads in private infrastructure while using the public cloud for non-sensitive services, balancing access with protection.
What industries benefit most from hybrid cloud?
Industries that benefit most from hybrid cloud include finance, legal, insurance, and healthcare. These sectors handle sensitive data, require strict compliance, and need both agility and control, making a hybrid an ideal model.
What is the best application deployment strategy in a hybrid cloud?
The best application deployment strategy in a hybrid cloud is a containerised microservices approach. It improves portability, enables seamless deployment across environments, and reduces infrastructure dependency.
Final Thoughts: Moving Forward with a Compliant Cloud Strategy
A strong hybrid cloud strategy gives regulated firms the structure to meet compliance, retain control, and scale securely. It supports long-term growth without sacrificing performance or operational agility.
Matrix Solutions offers cloud strategy services for law firms, financial industries, and compliance-driven industries. For an independent assessment or roadmap consultation, speak with our team for clear, pressure-free advice.




