No matter how careful you are, data loss can strike when you least expect it. Whether from accidental deletion, ransomware, or hardware failure, Australian businesses lose critical files every day. Without a proper data backup plan, the fallout can result in downtime, compliance issues, and lost client trust that’s hard to rebuild.
An effective backup approach uses the right combination of backup types, automated recovery systems, and secure storage, whether on-premises or in the cloud. With data volumes growing and compliance demands tightening, a structured backup plan is crucial to maintaining operational continuity and protection.
What Is Data Backup and Why Does It Matter?
Data backup is the process of creating a secure, restorable copy of business-critical files, applications, or systems. Its core purpose is to recover data after common disruptions, such as accidental deletion, cyberattacks, or hardware failure, events that often affect Australian businesses without warning.
In regulated industries, poor backup planning leads to risk beyond downtime. It can result in compliance breaches, financial penalties, and reputational damage, especially under APRA CPS 234 or the Privacy Act. Automated data backup and recovery reduce manual error, shorten recovery time, and protect customer trust.
Which Types of Data Backups Should You Know?
Different types of backup offer trade-offs in storage use, recovery time, and operational complexity. Understanding the core formats helps businesses apply the right backup mix to manage cost, reduce risk, and maintain continuity.
Each backup type supports recoverable, compliant data, especially when downtime or loss isn’t an option.
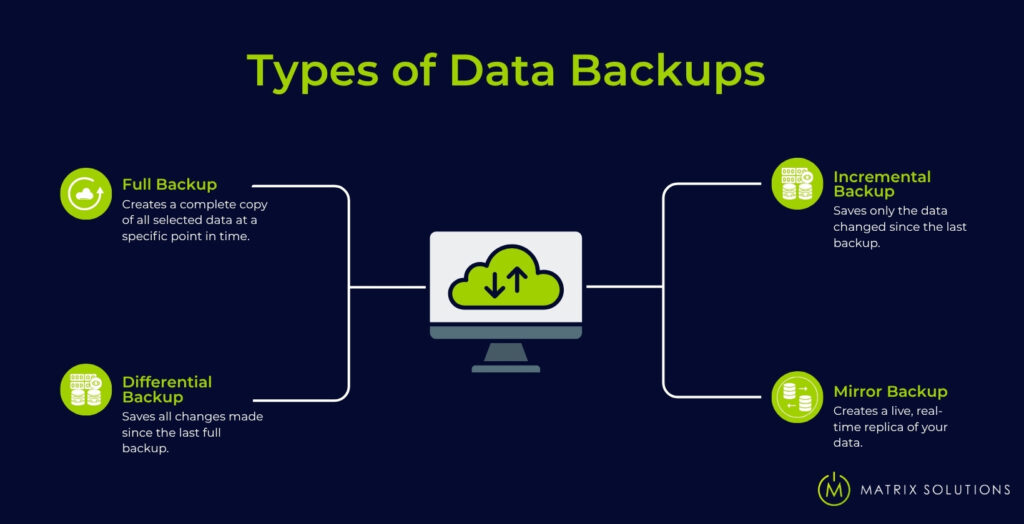
Full Backup
A full backup creates a complete copy of all selected data at a specific point in time. It’s easy to manage and fast to restore, but requires more storage space and time, especially with large datasets. Many businesses run full backups weekly to ensure total recovery is always possible.
Incremental Backup
An incremental backup saves only the data changed since the last backup. It runs quickly and uses less storage, but restores take longer as each change must be applied. It suits fast-paced teams with limited bandwidth or daily edits.
Differential Backup
A differential backup saves all changes made since the last full backup. It offers a balance between storage use and restore speed, requiring just two sets (full and latest differential) for recovery.
| Features | Incremental Backup | Differential Backup |
|---|---|---|
| Backup Scope | Since the last backup | Since the last full backup |
| Speed to Backup | Faster | Slower over time |
| Speed to Restore | Slower (requires full chain) | Faster (only two sets needed) |
| Storage Requirement | Lower | Higher |
| Recovery Risk | Higher if a backup set is missing | Lower; fewer sets required |
Mirror Backup
A mirror backup creates a live, real-time replica of your data. Any changes, including deletions, are instantly reflected. When it ensures high availability, it lacks version history and demands more storage. Businesses use it for critical systems requiring instant redundancy.
What Backup Storage Options Are Available Today?
Where your backups live matters just as much as how you create them. Speed, access, and disaster resilience all depend on storage location. Most businesses choose from three main options: local, cloud, or hybrid, each with distinct trade-offs in control, cost, and compliance.
Local Storage
Local storage keeps backup data on physical devices at your premises. It provides fast access and complete control, but comes with risks like theft, fire, or drive failure.
- USB drives: Affordable and portable, but easily lost or damaged.
- External hard drives (HDDs): Large capacity, ideal for bulk storage and quick restores.
- Network Attached Storage (NAS): Centralised for teams; supports office-wide access.
Local storage is best for fast recovery and offline access, but should be paired with off-site backups to guard against physical threats.
Cloud Storage
Cloud storage stores backup data on remote servers managed by third-party providers. It offers flexibility, scalability, and protection from local disruptions.
- AWS / Azure / Google Cloud: Trusted vendors with strong compliance and 99.9% uptime SLAs.
- SLAs: Guarantee recovery times and uptime through service agreements.
- Cost Model: Pay for what you use, based on storage, bandwidth, and operations.
- Scalability: Instantly expand without new hardware.
- Automation: Easily schedule, version, and encrypt backups using built-in tools.
Cloud storage is ideal for distributed teams that need always-on, off-site protection. Curious how managed cloud services could streamline your backups? Get a free consultation to explore your tailored options.
Hybrid Solutions
Hybrid cloud backup combines local speed with cloud redundancy. It provides fast on-site recovery for daily use and off-site security for disaster scenarios.
The hybrid model fits compliance-heavy sectors like legal, finance, and healthcare, where both local control and cloud resilience are required. Businesses get redundancy without compromising on access or data sovereignty.
How Often Should You Backup? Understanding RPO and RTO
You should back up your data as often as your business can’t afford to lose it. For rapidly changing environments, such as accounting platforms or legal case files, daily or even hourly backups may be necessary. If updates are infrequent, weekly or nightly schedules may be enough. The key is to define your RPO and RTO.
RPO (Recovery Point Objective) sets the maximum data loss your business can tolerate between backups. For example, if a legal firm updates files daily, its RPO should be 24 hours or less to avoid data loss. Shorter RPOs require more frequent backups.
RTO (Recovery Time Objective) defines how quickly systems must be restored after an outage. If a financial app must be operational within two hours, that becomes its RTO. Failing to meet RTO targets can disrupt services, breach SLAs, or cause compliance issues, especially in regulated sectors.
How Do I Choose the Right Backup Solution?
The right backup solution depends on how valuable your data is, how fast you need to recover it, and how involved you want to be. There’s no one-size-fits-all. Your choice should reflect risk tolerance, regulatory demands, and how often your systems change.
Cloud Backup vs External Drives
Choosing between cloud backup and external drives depends on your need for flexibility, control, and cost efficiency. Cloud options suit remote teams and compliance-heavy use cases. External drives are better for individual users or small teams with simpler recovery needs.
| Features | Cloud Backup | External Hard Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Subscription or usage-based billing | One-time hardware cost |
| Speed | Slower uploads/downloads (internet-dependent) | Fast, direct access and restore |
| Reliability | High availability, provider-managed redundancy | Risk of hardware failure, theft, or damage |
| Security | Encrypted in transit and at rest, off-site storage | User must manage encryption and physical access |
| Scalability | Grows with your business needs | Limited to device capacity; manual upgrades |
Automatic vs Manual Backups
Automatic Backup
✅ Runs on schedule without user input
✅ Reduces risk of human error
✅ Scales with changing data volumes
❌ May require paid software
❌ Needs initial setup and testing
❌ Relies on automation tools remaining active
Manual Backup
✅ Free or low-cost using basic tools
✅ Full control over what and when to back up
✅ No third-party dependency
❌ Easy to skip or forget
❌ Time-consuming and inconsistent
❌ Not practical for large or dynamic datasets
Tip: Automation becomes essential when file changes frequently or when recovery time must meet strict service-level agreements.
What Are the Steps to Create a Backup Strategy?
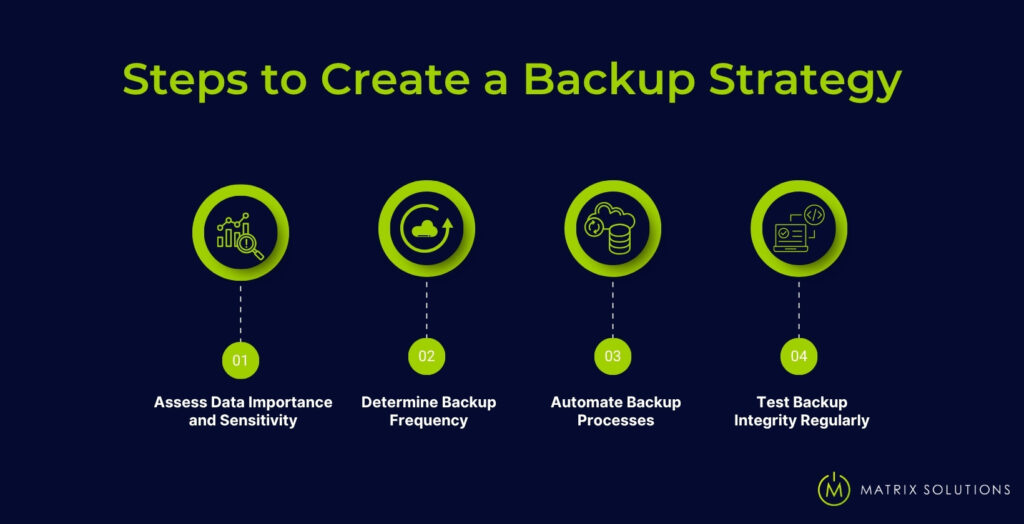
A solid data backup strategy protects your operations, limits downtime, and supports compliance, especially when the stakes are high. Follow these four clear steps to build a plan tailored to your business and recovery goals.
- Assess Data Importance and Sensitivity
Identify which files are critical, such as client records, accounting data, or daily creative assets. Classify based on business value and privacy risk to avoid wasting resources on non-essential data. - Determine Backup Frequency
Set your schedule based on how often the data changes. A design firm editing files daily might need hourly or daily backups. A law office logging updates weekly can back up less frequently. - Automate Backup Processes
Use data backup software or cloud tools to schedule and manage tasks automatically. This reduces manual work and ensures consistency, especially for teams with limited in-house IT resources. - Test Backup Integrity Regularly
Run restore tests monthly or quarterly to confirm backups function correctly. A corrupt file or failed backup can go unnoticed until it’s too late; regular testing prevents that risk.
Common Data Backup Mistakes You Should Avoid
Avoiding these mistakes can make the difference between a reliable recovery and permanent data loss. Each one adds unnecessary risk, but each can be easily fixed.
- Backing Up Only Once
Outdated backups leave recent data unprotected.
Fix: Set automatic, recurring backups based on how often your data changes. - Storing Backups in One Location
Keeping all backups on-site increases the risk of loss from theft, fire, or system failure.
Fix: Use both local and cloud backup for off-site protection. - Not Testing Your Backups
Corrupted or incomplete backups often go unnoticed until it’s too late.
Fix: Run scheduled test restores monthly or quarterly to verify integrity. - Ignoring Backup Encryption
Unencrypted backups are vulnerable to leaks or unauthorised access.
Fix: Encrypt backups both at rest and during transfer to keep data secure.
How Can You Keep Your Backups Safe with Encryption & MFA?
Encrypting your data keeps it secure, whether stored locally or in the cloud. Use AES-256 encryption for data at rest to block access, even if the storage device is stolen. For data in transit, apply SSL/TLS protocols to prevent interception during transfers, especially for cloud backups and remote sync tools.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) protects backup access points from unauthorised logins. Store encryption keys separately, limit admin access, and rotate credentials regularly. Combined with MFA, these controls lock down your backup environment, critical for compliance and protecting sensitive business data.
What Are Advanced Data Backup Options for Enterprise Use?
Enterprise environments require backup systems that ensure resilience, meet compliance, and maintain control at scale. These solutions must support automation, immutable storage, and audit trails to manage large data volumes and regulatory complexity.
Server & Business Systems
Enterprise-grade cloud data backup often includes image-based backups that capture the full server environment, including the operating system, apps, and configurations. This enables complete restoration after failure.
Virtualisation-aware tools like VMware or Hyper-V streamline backup performance and reduce downtime across workloads. Enterprises should use providers that offer SLA-backed recovery windows, high availability, and geographic redundancy to maintain continuity during outages.
Object Storage & Data Lakes
Object storage divides data into metadata-tagged units, ideal for large-scale, high-volume backups. Data lakes consolidate raw, unstructured data for centralised backup and long-term archiving.
Both integrate with enterprise backup platforms to enable automated ingestion, versioning, and policy-based retention, essential for compliance-heavy industries and analytics use cases.
FAQs About Backup, Recovery, and Cloud Storage
What is data backup and recovery?
Data backup and recovery is the process of copying data and restoring it after loss or damage. Backup creates duplicates; recovery restores them after deletion, malware, or hardware failure.
How to backup data in the cloud?
How to recover data from a lost phone without backup?
To recover data from a lost phone without backup, check if Google or iCloud sync was active. Without sync or prior backup, full data recovery is not possible.
How to backup app data to Google Drive?
To backup app data to Google Drive, go to Android settings > System > Backup. Enable “Backup to Google Drive” to automatically save app data, call logs, and device settings.
How to backup laptop data in Windows 11?
To backup laptop data in Windows 11, go to Settings > System > Storage > Advanced > Backup options. Use File History or Windows Backup to copy selected folders to a drive.
How to restore data after factory reset on Android without backup?
To restore data after factory reset without backup, check your Google account for synced items like contacts or photos. Recovery isn’t possible if syncing was disabled.
Wrapping Up: Your Data Backup Game Plan
Protecting your data starts with choosing the right storage, local, cloud, or hybrid, based on your recovery requirements and risk tolerance. Set clear RPO and RTO targets, automate your backups, and test regularly to ensure your systems work when it counts.
Secure backups using encryption and multi-factor authentication to reduce risk and meet compliance requirements. Now is the time to define your backup strategy and protect your systems before data loss turns into business disruption.
Ready to safeguard your critical data? Contact Matrix Solutions today for a tailored backup strategy that keeps your business running smoothly.




